{mnirs} is a package for reading, processing, and analysing data from muscle near-infrared spectroscopy (mNIRS) devices.
Installation
You can install the development version of {mnirs} from GitHub with:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("jemarnold/mnirs")Online App
A very basic implementation of this package is hosted at https://jem-arnold.shinyapps.io/mnirs/ and can currently be used for reading and pre-processing mNIRS data.
Usage
A more detailed vignette for common usage can be found here: Reading and Cleaning Data with {mnirs}
{mnirs} is currently in experimental development and functionality may change! Stay updated on development and follow releases at github.com/jemarnold/mnirs. {mnirs} is designed to process NIRS data, but it can be used to read, clean, and process other time series datasets which require many of the same processing steps. Enjoy!
read_mnirs() Read data from file
# remotes::install_github("jemarnold/mnirs") ## install development version
library(ggplot2) ## load for plotting
library(mnirs)
## {mnirs} includes sample files from a few mNIRS devices
example_mnirs()
#> [1] "artinis_intervals.xlsx" "moxy_intervals.csv"
#> [3] "moxy_ramp.xlsx" "portamon-oxcap.xlsx"
#> [5] "train.red_intervals.csv" "vo2master.csv"
## call an example mNIRS data file
file_path <- example_mnirs("moxy_ramp")
## rename channels in the format `new_name1 = "original_name1"`
## where "original_name1" should match the file column name exactly
data_table <- read_mnirs(
file_path,
nirs_channels = c(
smo2_right = "SmO2 Live", ## identify and rename channels
smo2_left = "SmO2 Live(2)"
),
time_channel = c(time = "hh:mm:ss"), ## date-time format will be converted to numeric
event_channel = NULL, ## left blank, not currently used in analysis
sample_rate = NULL, ## if blank, sample_rate will be estimated from time_channel
add_timestamp = FALSE, ## omit the date-time timestamp column
zero_time = TRUE, ## recalculate time values from zero
keep_all = FALSE, ## return only the specified data channels
verbose = TRUE ## show warnings & messages
)
#> ! Estimated `sample_rate` = 2 Hz.
#> ℹ Define `sample_rate` explicitly to override.
#> Warning: ! Duplicate or irregular `time_channel` samples detected.
#> ℹ Investigate at `time` = 211.99 and 1184.
#> ℹ Re-sample with `mnirs::resample_mnirs()`.
## Note the above info message that sample_rate was estimated correctly at 2 Hz ☝
## ignore the warnings about irregular sampling for now, we will resample later
data_table
#> # A tibble: 2,203 × 3
#> time smo2_right smo2_left
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0 54 68
#> 2 0.400 54 68
#> 3 0.960 54 68
#> 4 1.51 54 66
#> 5 2.06 54 66
#> 6 2.61 54 66
#> 7 3.16 54 66
#> 8 3.71 57 67
#> 9 4.26 57 67
#> 10 4.81 57 67
#> # ℹ 2,193 more rows
## note the hidden plot option to display time values as `h:mm:ss`
plot(data_table, label_time = TRUE)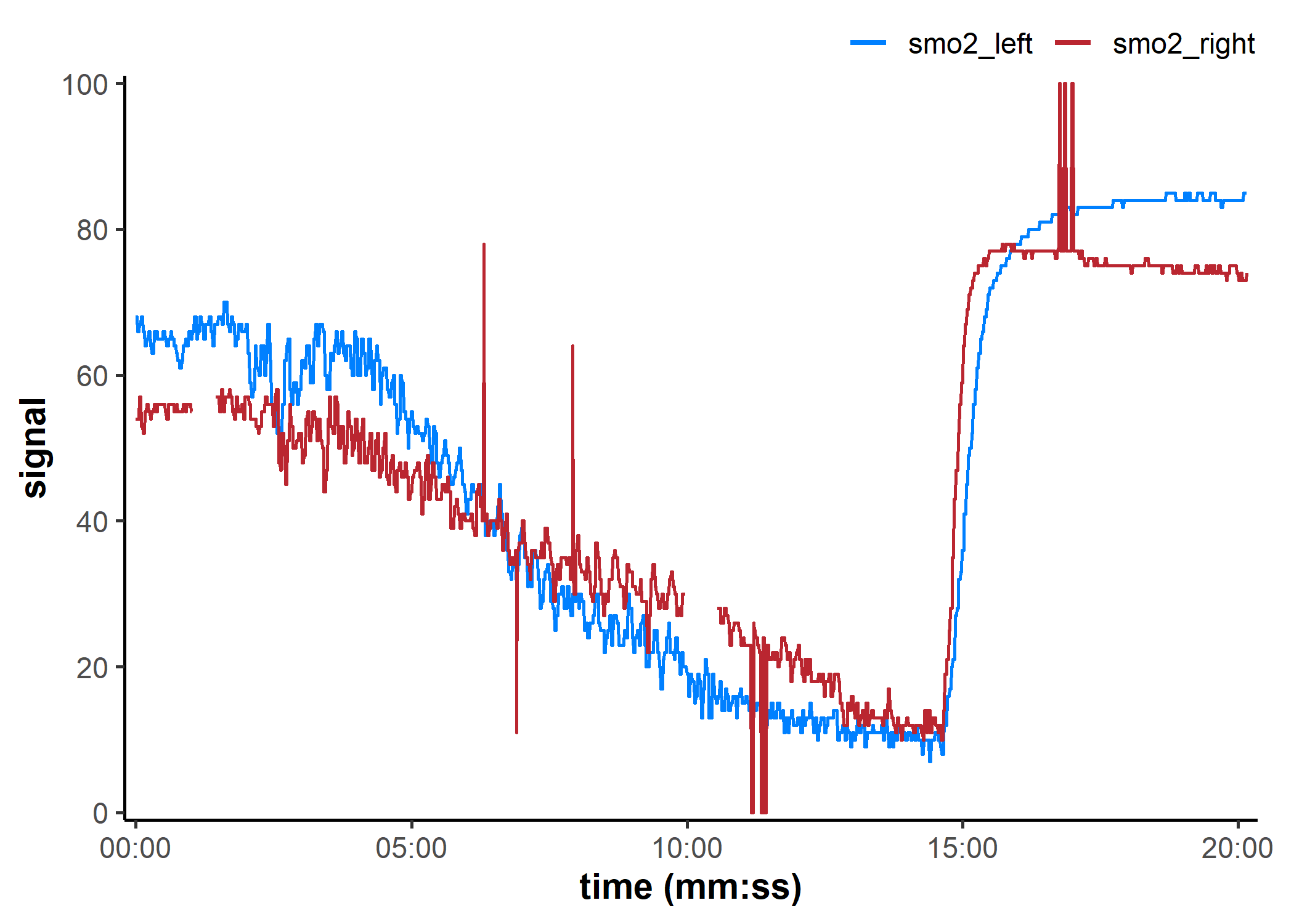
Metadata stored in mnirs data frames
## view metadata (omitting item two, a list of row numbers)
attributes(data_table)[-2]
#> $class
#> [1] "mnirs" "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"
#>
#> $names
#> [1] "time" "smo2_right" "smo2_left"
#>
#> $nirs_device
#> [1] "Moxy"
#>
#> $nirs_channels
#> [1] "smo2_right" "smo2_left"
#>
#> $time_channel
#> [1] "time"
#>
#> $sample_rate
#> [1] 2
replace_mnirs: Replace local outliers, invalid values, and missing values
data_cleaned <- replace_mnirs(
data_table, ## channels will be retrieved from metadata
invalid_values = 0, ## known invalid values in the data
invalid_above = 90, ## remove data spikes
outlier_cutoff = 3, ## recommended default value
width = 10, ## local window to detect local outliers and replace missing values
method = "linear", ## linear interpolation over `NA`s
verbose = TRUE
)
plot(data_cleaned, label_time = TRUE)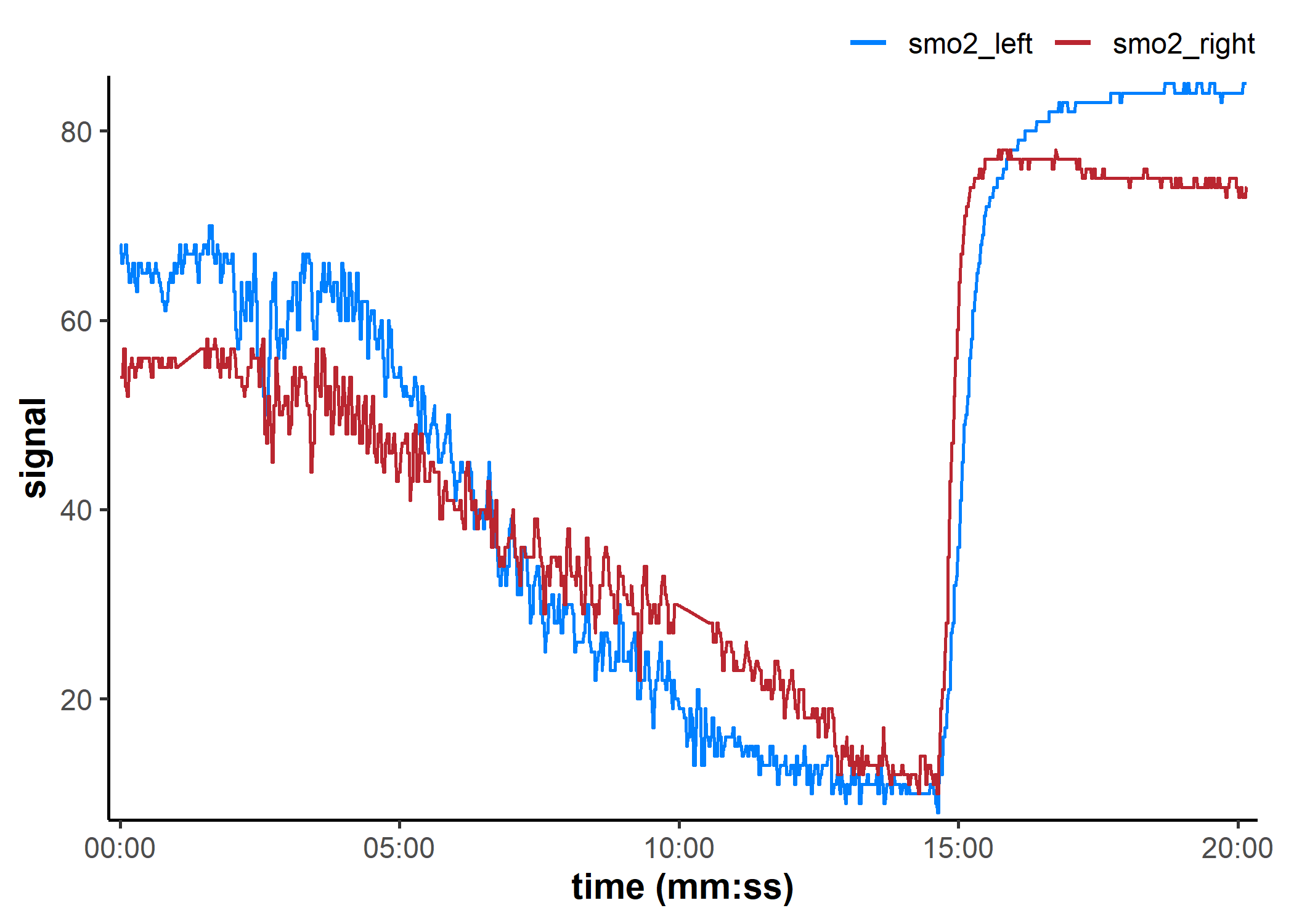
resample_mnirs(): Resample data
data_resampled <- resample_mnirs(
data_cleaned, ## channels retrieved from metadata
resample_rate = 2, ## the default `resample_rate = sample_rate` will resample to sample_rate
method = "linear", ## linear interpolation across any new samples
verbose = TRUE ## will confirm the output sample rate
)
#> ℹ Output is resampled at 2 Hz.
## note the altered "time" values from the original data frame 👇
data_resampled
#> # A tibble: 2,419 × 3
#> time smo2_right smo2_left
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0 54 68
#> 2 0.5 54 68
#> 3 1 54 67.9
#> 4 1.5 54 66.0
#> 5 2 54 66
#> 6 2.5 54 66
#> 7 3 54 66
#> 8 3.5 55.9 66.6
#> 9 4 57 67
#> 10 4.5 57 67
#> # ℹ 2,409 more rows
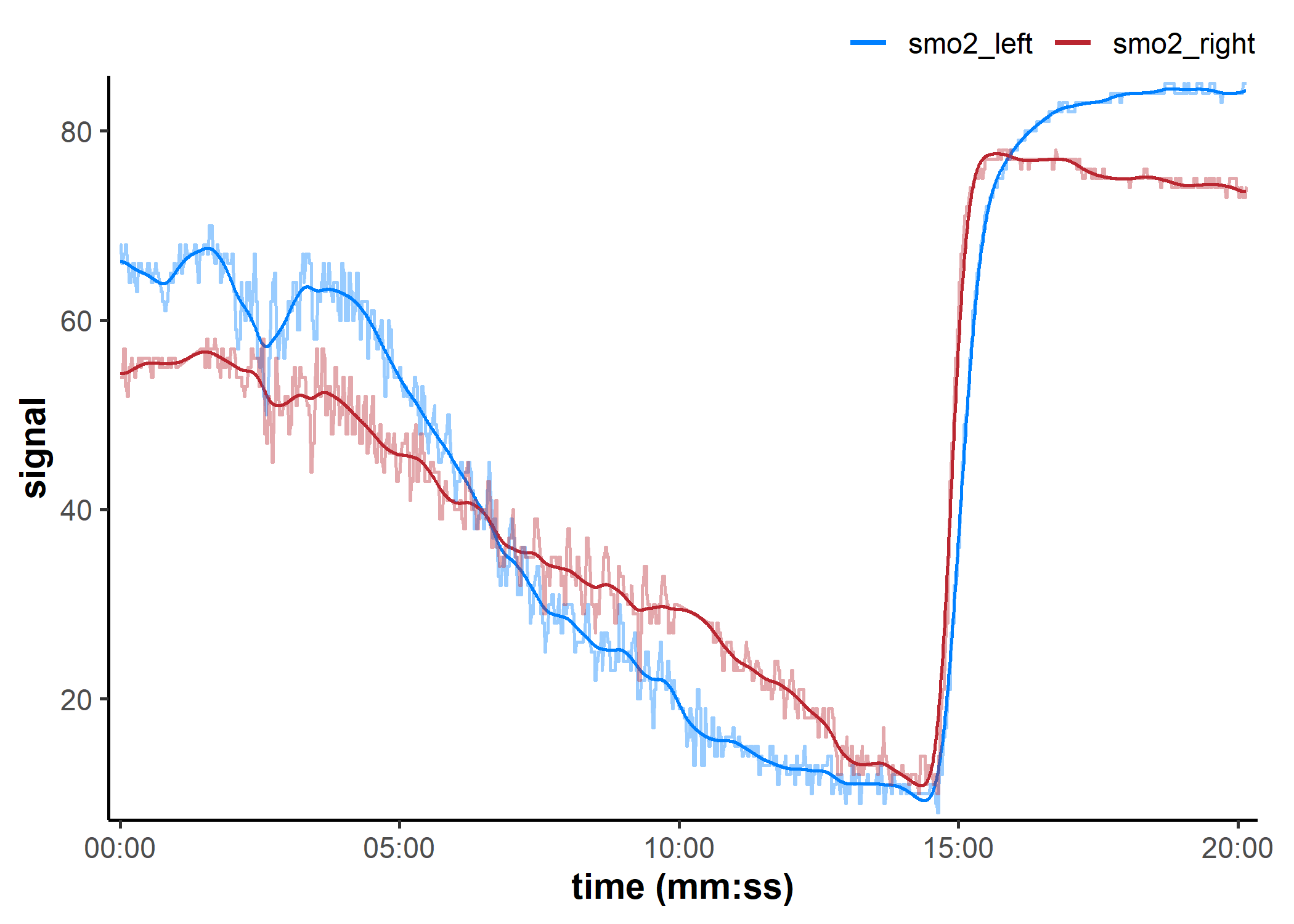
filter_mnirs(): Digital filtering
data_filtered <- filter_mnirs(
data_resampled, ## channels retrieved from metadata
method = "butterworth", ## Butterworth digital filter is a common choice
type = "low", ## specify a low-pass filter
order = 2, ## filter order number
W = 0.02, ## filter fractional critical frequency
na.rm = TRUE ## explicitly preserve any NAs
)
## we will add the non-filtered data back to the plot to compare
plot(data_filtered, label_time = TRUE) +
geom_line(
data = data_cleaned,
aes(y = smo2_left, colour = "smo2_left"), alpha = 0.4
) +
geom_line(
data = data_cleaned,
aes(y = smo2_right, colour = "smo2_right"), alpha = 0.4
)
shift_mnirs() & rescale_mnirs(): Shift and rescale data
data_shifted <- shift_mnirs(
data_filtered, ## un-grouped nirs channels to shift separately
nirs_channels = list(smo2_left, smo2_right),
to = 0, ## NIRS values will be shifted to zero
span = 120, ## shift the first 120 sec of data to zero
position = "first"
)
plot(data_shifted, label_time = TRUE) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0, linetype = "dotted")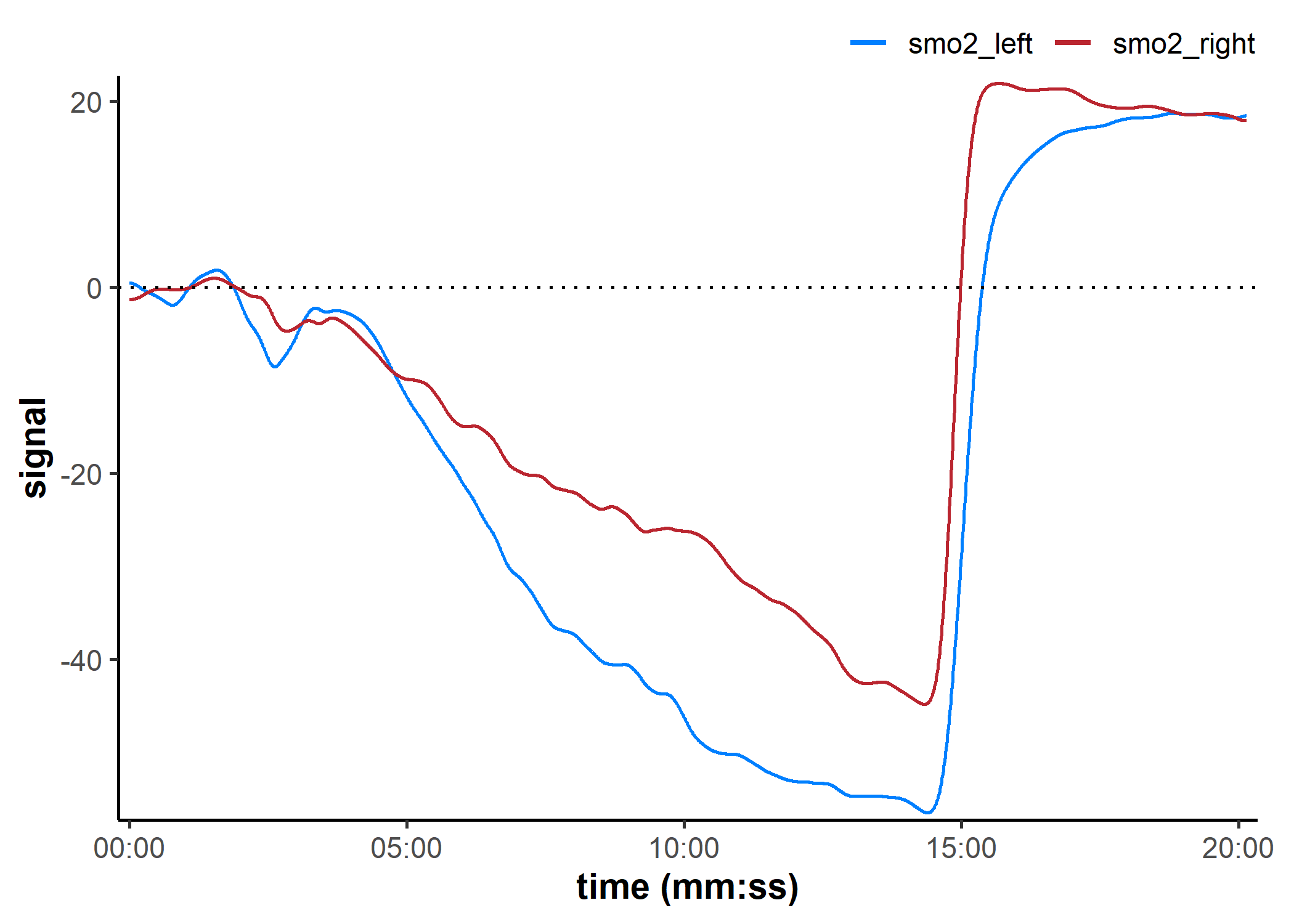
data_rescaled <- rescale_mnirs(
data_filtered, ## un-grouped nirs channels to rescale separately
nirs_channels = list(smo2_left, smo2_right),
range = c(0, 100) ## rescale to a 0-100% functional exercise range
)
plot(data_rescaled, label_time = TRUE) +
geom_hline(yintercept = c(0, 100), linetype = "dotted")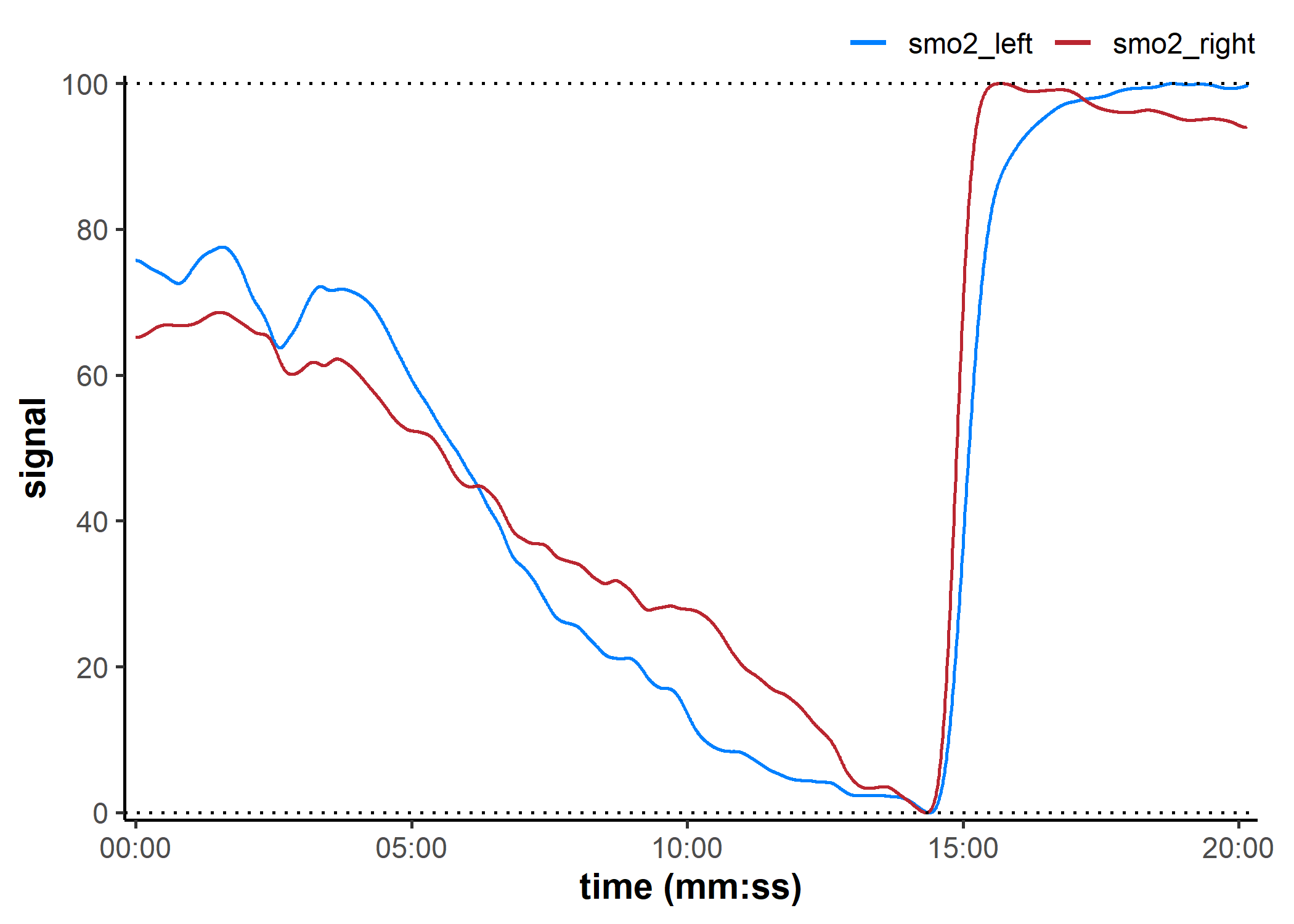
Pipe-friendly functions
## global option to silence info & warning messages
options(mnirs.verbose = FALSE)
## read, process, and plot an mNIRS file in one pipeline
read_mnirs(
example_mnirs("train.red"),
nirs_channels = c(
smo2_left = "SmO2 unfiltered",
smo2_right = "SmO2 unfiltered"
),
time_channel = c(time = "Timestamp (seconds passed)"),
zero_time = TRUE
) |>
resample_mnirs() |> ## default will resample to fix irregular samples
replace_mnirs(
invalid_above = 73,
outlier_cutoff = 3,
span = 7
) |>
filter_mnirs(
method = "butterworth",
order = 2,
W = 0.01,
na.rm = TRUE
) |>
shift_mnirs(
nirs_channels = list(smo2_left, smo2_right),
to = 0,
span = 60,
position = "first"
) |>
rescale_mnirs(
nirs_channels = list(c(smo2_left, smo2_right)), ## 👈 channels grouped together
range = c(0, 100)
) |>
plot(label_time = TRUE)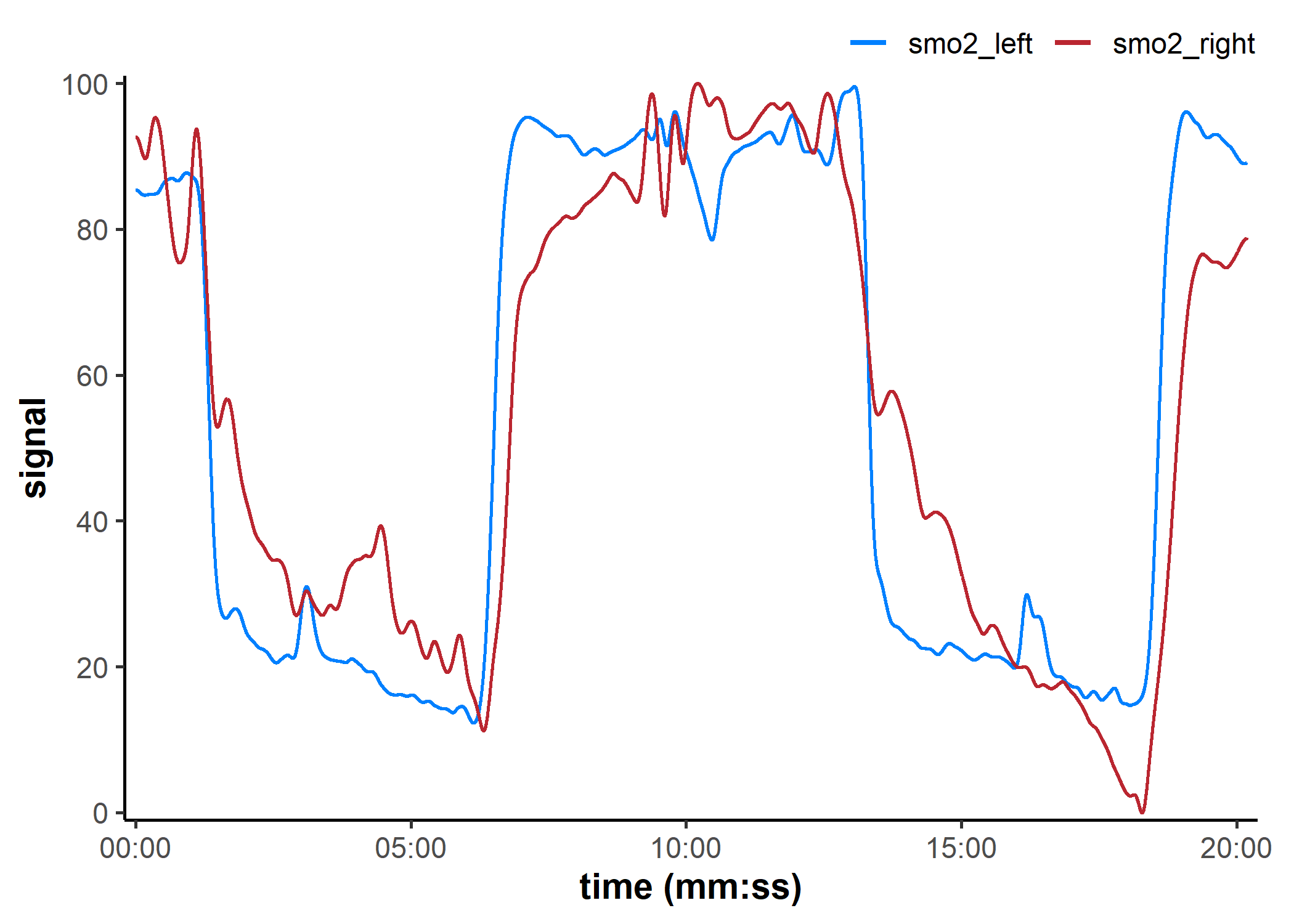
mNIRS device compatibility
This package is designed to recognise mNIRS data exported as .csv or .xls(x) files. It should be flexible for use with many different NIRS devices, and compatibility will improve with continued development.
Currently, it has been tested successfully with mNIRS data exported from the following devices and apps:
- Artinis Oxysoft software (.csv and .xlsx)
- Moxy direct export (.csv)
- PerfPro PC software (.xlsx)
- Train.Red app (.csv)
- VO2 Master Manager app (.xlsx)
Future {mnirs} development
Discrete interval processing
-
Process oxygenation kinetics
Monoexponential & sigmoidal curve fitting
non-parametric kinetics & slope analysis
Critical oxygenation breakpoint analysis
Generative codebots were used to assist with code optimisation. All code was thoroughly reviewed, revised, and validated by the package author.