Apply digital filtering/smoothing to numeric vector data within a data frame using either:
A cubic smoothing spline.
A Butterworth digital filter.
A simple moving average.
Arguments
- data
A data frame of class "mnirs" containing time series data and metadata.
- nirs_channels
A character vector of mNIRS channel names to operate on. Must match column names in
dataexactly. Retrieved from metadata if not defined explicitly.- time_channel
A character string indicating the time or sample channel name. Must match column names in
dataexactly. Retrieved from metadata if not defined explicitly.- sample_rate
A numeric value for the sample rate in Hz for
method = "butterworth". Will be taken from metadata or estimated fromtime_channelif not defined explicitly.- method
A character string indicating how to filter the data (see Details).
"smooth_spline"Fits a cubic smoothing spline.
"butterworth"Uses a centred Butterworth digital filter.
typemust be defined (see Details)."moving_average"Uses a centred moving average filter.
- spar
A numeric value defining the smoothing parameter for
method = "smooth_spline".- type
A character string indicating the digital filter type for
method = "butterworth"(see Details)."low"For a low-pass filter (the default).
"high"For a high-pass filter.
"stop"For a stop-band (band-reject) filter.
"pass"For a pass-band filter.
- order
An integer defining the filter order for
method = "butterworth"(defaultorder = 2).- W
A one- or two-element numeric vector defining the filter cutoff frequency(ies) for
method = "butterworth", as a fraction of the Nyquist frequency (see Details).- fc
A one- or two-element numeric vector defining the filter cutoff frequency(ies) for
method = "butterworth", in Hz (see Details).- width
An integer defining the local window in number of samples around
idxin which to perform the operation formethod = "moving_average". Between[idx - floor(width/2), idx + floor(width/2)].- span
A numeric value defining the local window timespan around
idxin which to perform the operation formethod = "moving_average". In units oftime_channelort, between[t - span/2, t + span/2].- na.rm
A logical indicating whether missing values should be preserved and passed through the filter (
TRUE). OtherwiseFALSE(the default) will throw an error if there are anyNAs (see Details).- verbose
A logical to display (the default) or silence (
FALSE) warnings and information messages used for troubleshooting.- ...
Additional arguments.
Value
A tibble of class "mnirs" with metadata
available with attributes().
Details
method = "smooth_spline"Applies a non-parametric cubic smoothing spline from
stats::smooth.spline(). Smoothing is defined by the parameterspar, which can be left asNULLand automatically determined via penalised log liklihood. This usually works well for smoothing responses occurring on the order of minutes or longer.sparcan be defined explicitly, typically (but not necessarily) in the rangespar = [0, 1].method = "butterworth"Applies a centred (two-pass symmetrical) Butterworth digital filter from
signal::butter()andsignal::filtfilt().Filter
typedefines how the desired signal frequencies are either passed or rejected from the output signal. Low-pass and high-pass filters allow only frequencies lower or higher than the cutoff frequencyWto be passed through as the output signal, respectively. Stop-band defines a critical range of frequencies which are rejected from the output signal. Pass-band defines a critical range of frequencies which are passed through as the output signal.The filter order (number of passes) is defined by
order, typically in the rangeorder = [1, 10]. Higher filter order tends to capture more rapid changes in amplitude, but also causes more distortion around those change points in the signal. General advice is to use the lowest filter order which sufficiently captures the desired rapid responses in the data.The critical (cutoff) frequency is defined by
W, a numeric value for low-pass and high-pass filters, or a two-element vectorc(low, high)defining the lower and upper bands for stop-band and pass-band filters.Wrepresents the desired fractional cutoff frequency in the rangeW = [0, 1], where1is the Nyquist frequency, i.e., half the sample rate of the data in Hz.Alternatively, the cutoff frequency can be defined by
fcandsample_ratetogether.fcrepresents the desired cutoff frequency in Hz, andsample_rateis the sample rate of the recorded data in Hz.W = fc / (sample_rate / 2).Only one of either
Worfcshould be defined. If both are defined,Wwill be preferred overfc.method = "moving_average"Applies a centred (symmetrical) moving average filter in a local window, defined by either
widthas the number of samples aroundidxbetween[idx - floor(width/2),idx + floor(width/2)]. Or byspanas the timespan in units oftime_channelbetween[t - span/2, t + span/2]. Specifyingwidthis often faster thanspan. A partial moving average will be calculated at the edges of the data.
Missing values (NA) in nirs_channels will cause an error for
method = "smooth_spline" or "butterworth", unless na.rm = TRUE.
Then NAs will be preserved and passed through in the returned data.
Examples
options(mnirs.verbose = FALSE)
## read example data
data <- read_mnirs(
file_path = example_mnirs("moxy_ramp"),
nirs_channels = c(smo2 = "SmO2 Live"),
time_channel = c(time = "hh:mm:ss")
) |>
replace_mnirs(
invalid_values = c(0, 100),
outlier_cutoff = 3,
width = 10
)
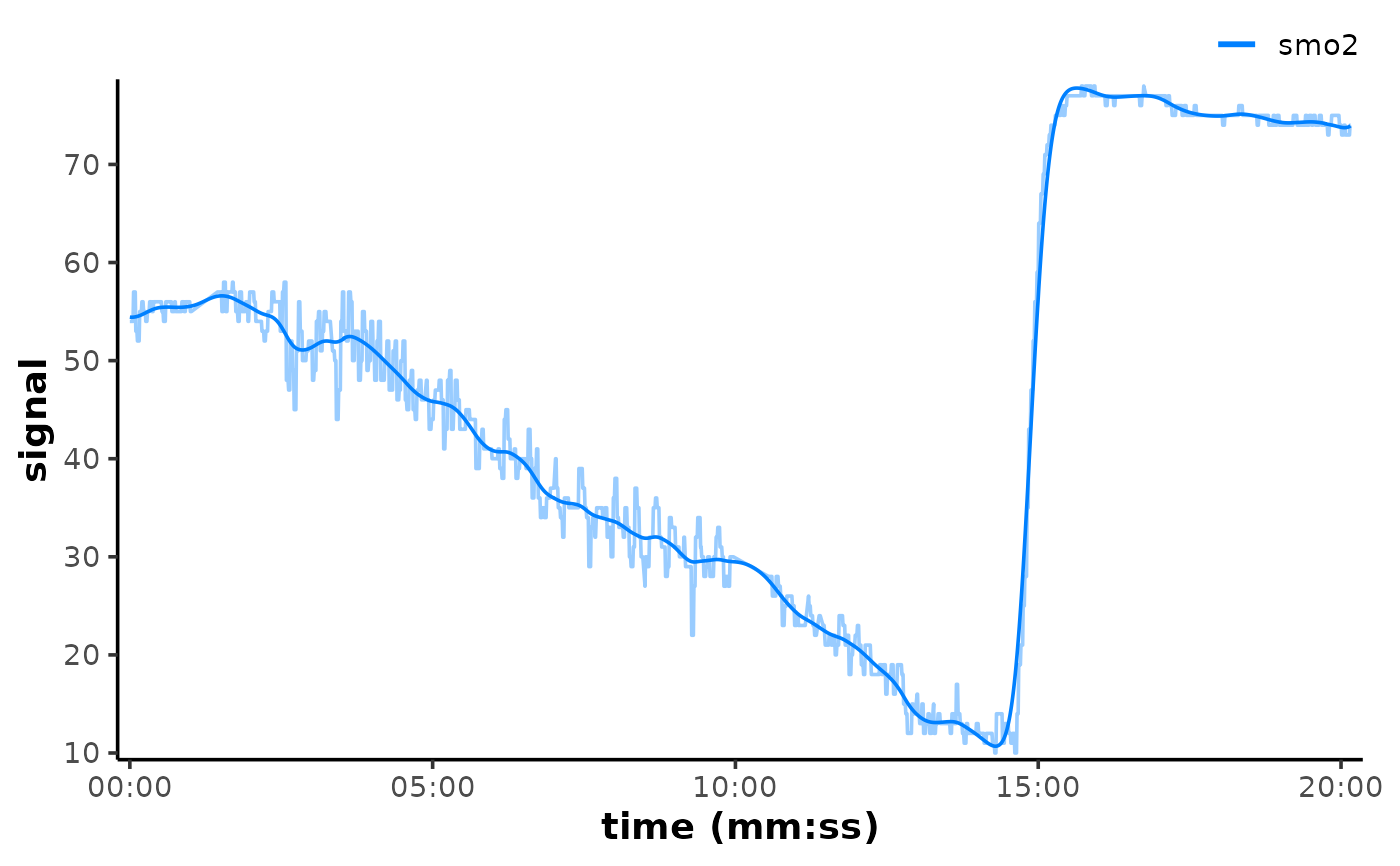
data_filtered <- filter_mnirs(
data,
method = "butterworth", ## Butterworth digital filter is a common choice
type = "low", ## specify a low-pass filter
order = 2, ## order is the number of filter passes
W = 0.02, ## fractional critical frequency
na.rm = TRUE ## explicitly preserve any NAs and avoid errors
)
library(ggplot2)
## plot filtered data and add the raw data back to the plot to compare
plot(data_filtered, label_time = TRUE) +
geom_line(
data = data,
aes(y = smo2, colour = "smo2"), alpha = 0.4
)